Adaptive Training of Grid-Dependent Physics-Informed Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks
In this open-access paper, which can be found here, we present a novel adaptive training framework for Physics-Informed Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (PIKANs). Our JAX-based computational framework significantly accelerates training by up to 84x compared to previous implementations and achieves enhanced accuracy in solving Partial Differential Equations (PDEs) with fewer parameters.
What Are Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs)? Link to heading
KANs are a class of neural networks inspired by the Kolmogorov-Arnold representation theorem. Unlike traditional multilayer perceptrons (MLPs), KANs feature learnable activation functions at their edges and a summation operation at their nodes, providing greater interpretability and possibly efficiency. These properties make KANs particularly suited for scientific and engineering applications, such as solving PDEs.
From PINNs to PIKANs Link to heading
Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) revolutionized the way we solve PDEs by embedding physics constraints directly into a neural network’s loss function, bypassing traditional grid-based methods. While PINNs typically use MLPs as their underlying architecture, PIKANs build on this framework by replacing MLPs with KANs. This substitution introduces several advantages, including a smaller parameter footprint, because KANs are able to capture the dynamics of the problem using significantly shallower and narrower architectures. Additionally, they allow for more adaptability than MLPs, thanks to their inherent grid-dependent nature.

Key Findings Link to heading
Enhanced Training Speed: Using our jaxKAN implementation, our framework achieved training times up to two orders of magnitude faster than existing methods.
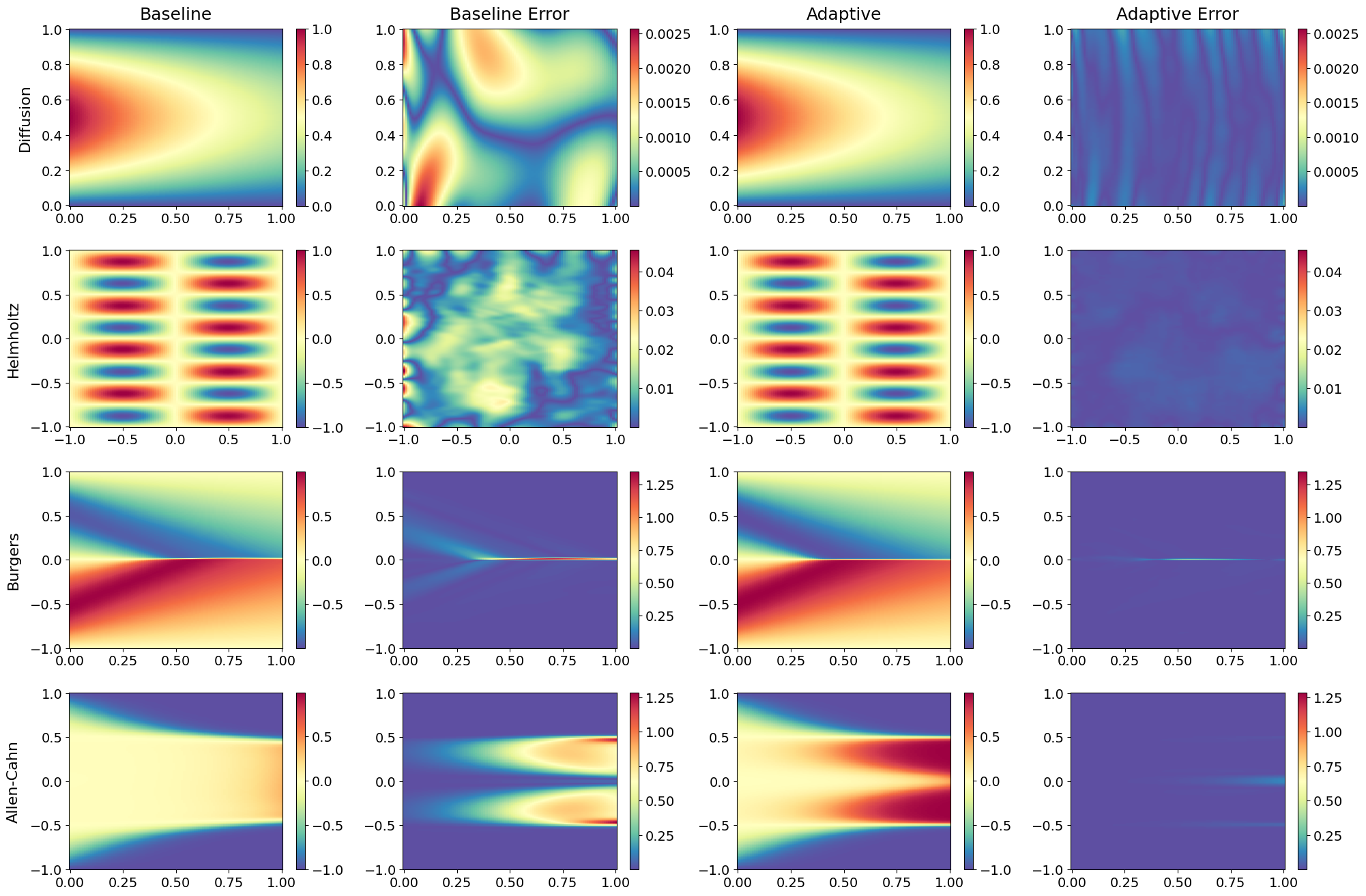
Improved Accuracy: With adaptive techniques like grid-dependent training, loss re-weighting, and collocation point resampling, PIKANs reduced relative $L^2$ errors by up to 43% compared to their vanilla versions.
Efficient Architectures: Our PIKANs performed on par or better than architectures with up to 8.5x more parameters.
Abrupt Peaks Smoothening: We proposed an adaptive optimizer state transition which alleviated the problem of abrupt peaks appearing in the loss function’s graph after grid updates.
Below is a visualization showcasing the adaptive PIKAN solutions for four PDEs alongside their reference solutions and baseline implementation. The results illustrate the significant improvements achieved through the proposed adaptive training methods.
@article{10763509,
author = {Rigas, Spyros and Papachristou, Michalis and Papadopoulos, Theofilos and Anagnostopoulos, Fotios and Alexandridis, Georgios},
journal = {IEEE Access},
title = {Adaptive Training of Grid-Dependent Physics-Informed Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks},
year = {2024},
volume = {12},
pages = {176982-176998},
doi = {10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3504962}
}